Chlorophyll is the most important product of photosynthesis, and chlorophyll content is also one of the important physiological indicators of plants. Therefore, it is of great significance to study the extraction method of chlorophyll. Chlorophyll content determination methods are generally spectrophotometric, living chlorophyll method and photoacoustic spectroscopy, the most widely used spectrophotometric method. Because of the different methods used for extracting chlorophyll, there are many methods for the determination of chlorophyll. Chlorophyll detectors are widely used in the early detection of chlorophyll. However, due to the slag removal after grinding, this method has a large workload, many steps, and is easily exposed to photo-oxidation. Extraction and determination of a large number of samples in the field. By comparing the extraction of several different mixed extracts, the best method to determine the content of chlorophyll in cotton leaves was acetone extraction. The effects of different ratios of acetone, ethanol and water on the leaching efficiency were studied, and the feasibility of chlorophyll extraction using the mixture was demonstrated. The results showed that there was a synergistic effect of extracting chlorophyll from the mixture of acetone and ethanol, and the extraction efficiency was the best when they were mixed in equimolar mixture. It was considered that the effect of extracting chlorophyll with acetone ethanol (2:1) mixture was better. Based on previous studies, the experiment further explored the advantages and disadvantages of each method for chlorophyll content determination and the steps for rapid determination, providing a basis for the determination of large-scale chlorophyll content in field of pakchoi.
1 Materials and methods 1.1 Test materials Wash fresh cabbage leaves, air dry, and remove large veins. A 752S UV-visible spectrophotometer was used for the test. Acetone, 95% ethanol, and other reagents were all analytically pure. The test water was secondary water.
1.2 Test methods 1.2.1 Tests for extracting effects of different extracts Weigh 0.5 g of test material into test tubes, cut the leaves into 2 mm pieces, and immediately use acetone grinding and direct extraction (4 kinds of extracts) at room temperature. : 95% ethanol, acetone, ethanol (1:1), 95% ethanol, acetone, water (4.5:4.5:1), acetone, 95% ethanol (2:1)) Chlorophyll was extracted 3 times. The leaching was performed in the dark. Each test tube was filled with 10 mL of extract solution and shaken from time to time. The leaves became white. After about 14 h, the volume was 25 mL, and the absorbance was measured. The absorbance was measured at 645 nm and 663 nm, respectively, using the corresponding reagents at room temperature. The Arnon formula was used to calculate the chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b contents. Chlorophyll a (chla) content (mg/g) = (12.7 x A663 - 2.697 x A645) 7 x V/ (1000W); Chlorophyll b (chb) content (mg/g) = (22.77 x A645 - 4.687 x A663) 7×V/(1000W); total chlorophyll content (mg/g)=chla content+chlb content. Where A663, A645 are the absorbance values ​​at the corresponding wavelengths, V is the volume of the extract, and W is the mass of the blade taken.
1.2.2 Extraction effect and stability test of different extracts: Light stability test: After the sample is placed in the light, the chlorophyll content in the extract is determined again after 1, 3, and 5 hours of storage. The stability of the extract. Then use the leaf area meter to measure the area of ​​the cabbage leaves. Thermal stability test: Extract the chlorophyll extraction test, take 10 mL of the extract in a stoppered test tube, and heat in a water bath at 30, 50, and 70°C, respectively. Under conditions of incubation for 10 min and cooling to room temperature, the chlorophyll content was determined.
2 Results and analysis 2.1 Comparison of extraction efficiency and photostability of different extraction methods Table 1~5 shows that five different extraction methods have the highest total chlorophyll content obtained by the extraction (ethanol: acetone = 1:1) extraction method ( 0.438); ethanol extraction is the lowest (only 0.305); the other three extraction methods are not the same. Degradation values ​​were fastest with acetone milling (0.263); mixed liquor (ethanol B acetone B = 4.5:4.5:1) followed by extraction (0.208); mixed liquor (ethanol: acetone = 2:1) and mixed The solution (ethanol: acetone = 1:1) extraction was slower (0.185 and 0.165, respectively). It shows that the acetone grinding method may damage the chloroplast due to the grinding process, and the extracted chlorophyll is extremely unstable under light. The chlorophyll content of the mixed liquor (ethanol:acetone=2:1) ​​and the mixed liquor (ethanol:acetone=1:1) can obtain high chlorophyll content, and it also has good stability under light.
With the extension of the time of light exposure, all the extraction methods have chlorophyll a degradation values ​​much faster than chlorophyll b. The chlorophyll a degradation values ​​of different extraction methods varied from 0.133 to 0.288, while the chlorophyll b degradation values ​​varied from 0.020 to 0.053. In addition, the chla/chlb values ​​of each extraction method show a decreasing trend with the extension of the light exposure time, which can also be reflected in
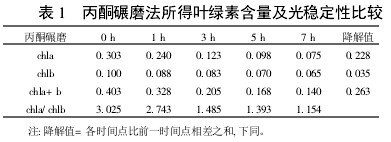
Table 1 Comparison of chlorophyll content and photostability obtained by acetone milling
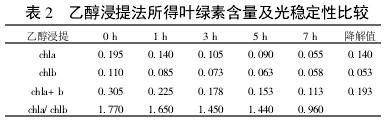
Table 2 Comparison of chlorophyll content and photostability obtained by ethanol extraction
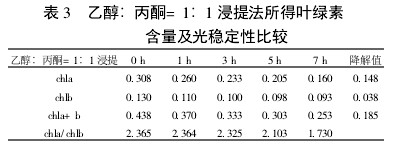
Table 3 Comparison of chlorophyll content and photostability of ethanol: acetone = 1:1 extraction
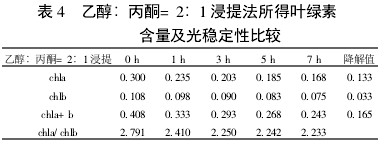
Table 4 Comparison of chlorophyll content and photostability of ethanol: acetone = 2:1 extraction
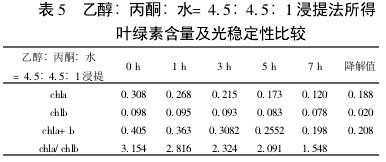
Table 5 Ethanol:acetone:water =4.5:4.5:1 Extraction of chlorophyll content and photostability The chlorophyll a degradation rate is faster than chlorophyll b. This shows that in visible light, chlorophyll a is more degradable than chlorophyll b.
2.2 Comparison of the thermal stability of the extraction methods for different extracts From Table 6, it can be seen that the contents of chla, chlb, and Chla+b obtained by each extraction method decrease with increasing temperature. At 70°C, the ethanol extraction method is almost completely changed. Brown, while other treatments still can see green, in which the content of Chla+b is highest with the mixed liquor (ethanol: acetone = 1:1). The results showed that the content of chlorophyll obtained by single ethanol extraction was low and unstable, while the content of chlorophyll after the addition of acetone was increased and stable. The value of chla/chlb for each treatment also decreases with increasing temperature, indicating that chlorophyll a is more degradable than chlorophyll b at high temperatures, consistent with changes in light.
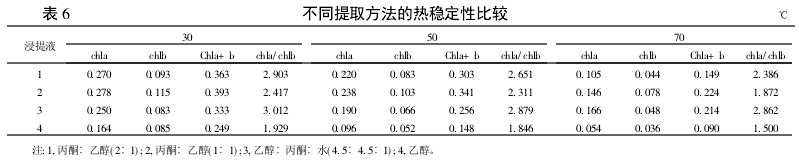
Table 6 Comparison of thermal stability of different extraction methods 3 Summary and discussion The mixed liquor extraction method not only has higher chlorophyll content than ethanol extraction method, but also has better stability to light and heat than ethanol extraction method. Among them, the highest chlorophyll content was obtained by leaching with a mixture (ethanol:acetone=1:1). The chlorophyll content obtained by single ethanol leaching was low and unstable in the test. When acetone was added, the extraction of chlorophyll was more complete and the stability was better. The results showed that there was a synergistic effect of extracting chlorophyll from the mixture of acetone and ethanol, and the extraction efficiency was the best when they were mixed in equimolar mixture, which was consistent with the research results.
The acetone grinding method in the test can also obtain higher chlorophyll content, which is different from previous research results. The specific reasons need to be further studied.
However, this method is also undesirable because the chlorophyll extracted by the grinding method is extremely unstable under light. Based on the comprehensive analysis, the best extracting method of Chinese cabbage chlorophyll was the extraction method of mixed liquor (ethanol:acetone=1:1), followed by the extraction of mixed liquor (ethanol:acetone:water=4.5:4.5:1). The mixed liquor (ethanol: acetone = 2:1) extraction method, acetone grinding method and ethanol extraction method were the worst.
With the increase of the time of light exposure and the increase of temperature, all the extraction methods have chlorophyll a degradation values ​​much faster than chlorophyll b. It shows that the degradation rate of chlorophyll a is faster than that of chlorophyll b, which is consistent with the research results. The results showed that the key to affecting the extraction efficiency of chlorophyll was the extraction speed and stability of chlorophyll a.
Our matting agents' main material is silica dioxide, a natural material that can be found in quartz or sand.
We change the original silica dioxide's chemical parameters to make it turn into different types silica
Matting Agent that are suitable to use in different using areas.
We provide various types of hydrophilic Fumed Silica that are used in wood coatings, inks, industrial coatings, coil coatings,plastic coatings, UV curing coatings, leather coatings, E-coats ,matte paper coatings and powder coatings.
We focus on the matting agent about 25 years, knowing exactly the customer`s requirement, and have most experience to offer service and technical solution to the customers. We have strict control of the quality; the physical index and performance are strictly tested before delivery. Will ensure that stable products of different batch. Compare to International and the other Chinese Supplier, our products has better performance, stable quality and cost efficient.

Hydrophilic Fumed Silica,Hydrophilic Silica,112945-52-5 Hydrophilic Pyrogenic Silica,Fumed Silicon
Guangzhou Quanxu Technology Co Ltd , https://www.silicamattingagent.com