Fractal Theory to Study the Results of Peach Tree Roots
The study of plant roots is not only because the root system can provide the water, nutrients, and nutrition needed by plants, but also is an important criterion for judging the quality of plant growth and health. Both the farmland and research institutes will use root analysis systems, Root analyzers and other testing instruments. This method is simple and the results are relatively accurate, so it is very extensive. Today we are introducing another method of root analysis. The concept of the fractal analysis of the root system was proposed by the French mathematician Mandelbrot in the mid-1970s. Fractal structures generally have intrinsic geometric regularity—a proportion of self-similarity, that is, for any part of the microscopic or enlarged, the degree of irregularity is the same, and at the same time almost all the fractals are invariant to the displacement, that is, its Each part shifts, rotates, shrinks, etc. and is statistically similar to any other site. This regularity of fractals is characterized by fractal dimensions. There are many definitions of fractal dimensions, and the most widely used is the box dimension. The box dimension is defined as: Let fractal group A belong to Rn. In Euclidean distance, use small box with side length 2n to contain A immediately next to it. Let Nn(A) be the minimum number of boxes required to contain A, FD =lim1nNrOA) is the set of box dimensions.
Fractals can be used not only to describe the morphological structure of the root system, but also to describe the changes in the total root length and total dry weight, as well as the growth status of the plant's aerial parts. In the past, the research on the fractal of the root system mainly focused on the situation when the environmental conditions were suitable. There were few researches on the fractal characteristics when the environment changed. This paper mainly discusses the effect of water stress on the fractal characteristics of root system by studying the fractal characteristics of root system under different water conditions.
Materials and Method
The experiment was conducted at the Experimental Garden of the Beijing Forestry Fruit Research Institute in 2002. The test material was a 4-year-old potted nectarine (Prunspersica var. nectarine Maxim), and the cultivar was Ruiguang No. 5, which was divided into 5 treatments: (1) normal irrigation and water potential Between 0.1-0.2MPa; (2) Moderate drought, water potential controlled at 0.8-1.2MPa; (3) Severe drought, water potential at a level of 2.0}-2.5MPa; (4) Over-irrigation, water potential> -0.1Mpa, poured The amount of water is equivalent to 3 times of normal irrigation; (5) 1 month after severe drought, then normal irrigation for 1 month.
Each treatment was repeated 8 times, per plant plot. The soil water potential was measured using a plaster block method, and soil moisture was controlled in conjunction with quantitative watering. After two months of treatment, the fractal dimension of the root system was measured in mid-July using the method of Gong Yiqin et al. [3], and 8 trees were processed for each treatment, and each tree was repeated 3 times 5 times. The diameter of the last root system was measured with a vernier caliper and repeated 80 times. The average value (0.17mm) was brought into the equation to determine the length of each treatment root (L = Nr, the root of each tree was dried, and Daping was used. Weigh dry weight.
results and analysis
1 Fractal dimension under different moisture conditions
The fractal dimension (FD>, root abundance (LogI), correlation coefficient of regression equation (R>, total root length (L) and total root weight (W>) As can be seen from Table 1, the fractal dimension of the rewatered root system is the largest, and the fractal dimension of the leech treatment is the smallest, and the severe drought treatment is less than moderate drought treatment, and the moderate drought treatment is less than normal watering. Although the absolute values ​​of the dimensions are not much different, because the root length is exponentially related to the fractal dimension, the small change in the fractal dimension can cause a drastic change in the root length.
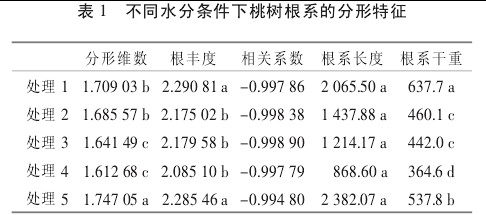
2 Root length under different moisture conditions
From Table 1, it can be seen that the soil moisture status has a significant impact on root length, including rehydration> normal watering> moderate drought> severe drought> waterlogging treatment. It may be due to the exponential relationship between the length of root system and FD and logI}. The variation of error is relatively large, so the analysis of variance is not significant. The root length of the rehydration treatment was significantly greater than other treatments, possibly because of a "compensation effect" after rehydration, which stimulated the occurrence of new roots. The root system of leeches treatment has deteriorated due to the permeability of the soil, and the occurrence and growth of the root system has been inhibited. Some root systems have died. Root length is very sensitive to FD. It can be seen from Figure 1 that when FD increases from 1.6 to 1.8, the length of the root system increases by 125.9%. Similarly, the diameter of the last primary root system also has a great influence on the root length. Figure 2 We can see that when the diameter of the last root system is reduced from 1mm to 0.1mm, the total root length increases from 99.96m to 5115.29m. For the treatment of normal watering, the root length of >1mm accounts for the root system. The total length of 4.8%, and <1mm of the root system accounted for 95.2% of the total length o4 Discussion Through the above analysis we can see that there are obvious differences in the fractal dimension of peach root system under different water conditions, this difference is mainly due to new roots The occurrence and growth conditions are determined, and they are concentrated on the impact on the length of the root system. The fractal dimension of mink treatment is the smallest, and drought stress also makes the fractal dimension smaller. After drought, rehydration can make the fractal dimension larger.
Results and discussion
The fractal dimension of wheat roots differs in different growth stages and different soil depths, and the fractal dimension of wheat forced by drought stress becomes smaller. Fractal analysis of roots in wood research is carried out in two dimensions, and the analysis we make is static. The roots of peach trees should have different fractal dimensions at different stages of growth and development under different environmental conditions. .
Biological Virgin Pulp Making System
The lack of paper making raw materials is a common problem, the use of seasonal growth plants or wild trees etc for the paper pulp is an effective solution.However, using this material pulping will produce a lot of black liquor containing inorganic compounds, how can get more fiber pulp, low investment to processing black liquor which can let it reach the water recycling or reach the discharge standard of environmental protection, it has been a worldwide problem all the time.

Pulp Making Machine,Virgin Pulp Making Machine,Biological Virgin Pulp Making Machine,Biological Virgin Pulp Making System
Dandong Tianshin Automatization Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.tianshinmachine.com